Set Token Allowances
To allow a third-party service—such as the 0x API—to move your ERC-20 tokens, you must first grant a token allowance. When using 0x APIs, this means approving either AllowanceHolder or Permit2 to move tokens on your behalf.
Which contract to approve depends on the API endpoint you’re using:
The wallet holding the tokens (taker) must approve the contract address returned in issues.allowance.spender or allowanceTarget from the /price or /quote response.
No allowance is needed for wrapping/unwrapping ETH (e.g., WETH ⇄ ETH). In
these cases, allowance is null.
Allowance Target vs. Entry Point
In API v2, allowance management and swap execution are handled by different contracts.
1. Allowance Target Contract
- Purpose: The contract where token approvals are set.
- Which contract: Permit2 (
/swap/permit2) or AllowanceHolder (/swap/allowance-holder), depending on the approval method. - How to find it: Returned in
issues.allowance.spenderorallowanceTarget.
2. Entry Point Contract
- Purpose: Executes swaps; send the
datapayload here. - Which contract: 0x Settler (
/swap/permit2) or AllowanceHolder (/swap/allowance-holder), depending on the approval method. - How to find it: Returned in
transaction.to.
This separation enhances security by isolating allowance management from swap execution.
-
NEVER set an allowance on the Settler contract. Doing so may result in unintended consequences, including potential loss of tokens or exposure to security risks. The Settler contract does not support or require token allowances for its operation. Setting an allowance on the Settler contract will lead to misuse by other parties.
-
ONLY set allowances on AllowanceHolder or Permit2 contracts, as indicated by the API responses.
-
The correct allowance target is returned in
issues.allowance.spenderorallowanceTarget.
Example response from /swap/permit2/quote will return back the contract address if an allowance needs to be set:
How to Set a Token Allowance
You can approve allowances programmatically or via UI:
Using wagmi
wagmi provides a clean interface for reading and writing allowances:
- Read current allowance using
useReadContract. - Simulate and write approval with
useSimulateContractanduseWriteContract. - Wait for transaction confirmation using
useWaitForTransactionReceipt.
Here’s a minimal example:
For a full implementation, see:
-
AllowanceHolder
-
Permit2
Using Etherscan
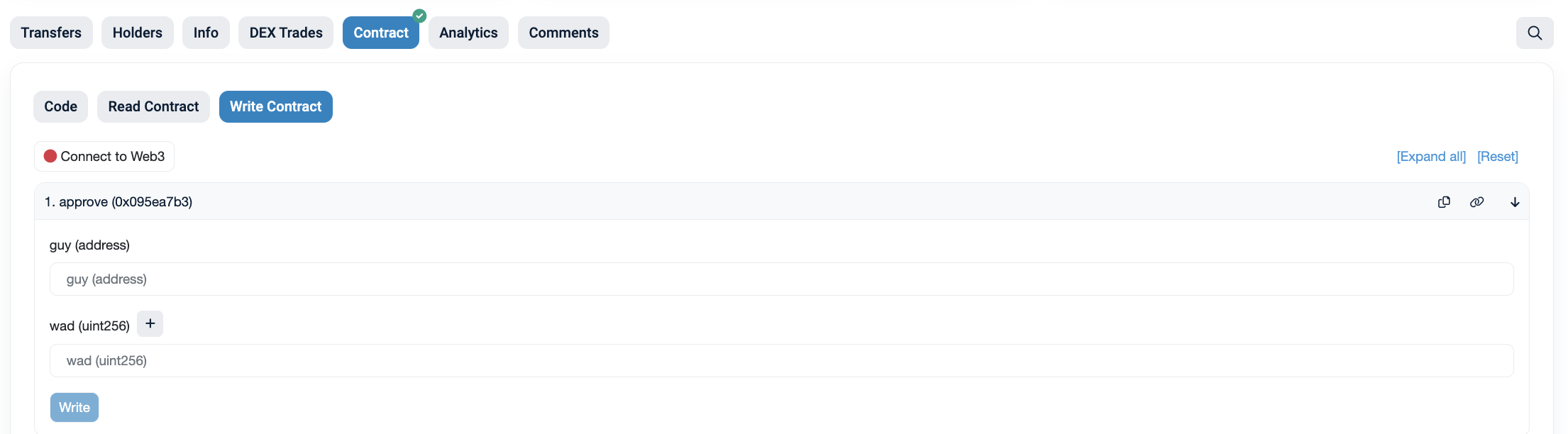
You can manually set allowances via Etherscan:
- Navigate to the token’s contract page (e.g., WETH).
- Go to Write Contract > approve
- Enter:
_spender: theissues.allowance.spenderaddress from the API._value: the maximum uint256 value (2^256 - 1).
Revoking Allowances
To revoke an allowance, you will need to set the allowance to 0. This can be done programmatically or through a UI such as https://revoke.cash/ .
Common Issues
When setting the token allowance, make sure to provide enough allowance for the buy or sell amount as well as the gas; otherwise, you may receive a ‘Gas estimation failed’ error.